Kursus „Integraal. Tasandilised kujundid”
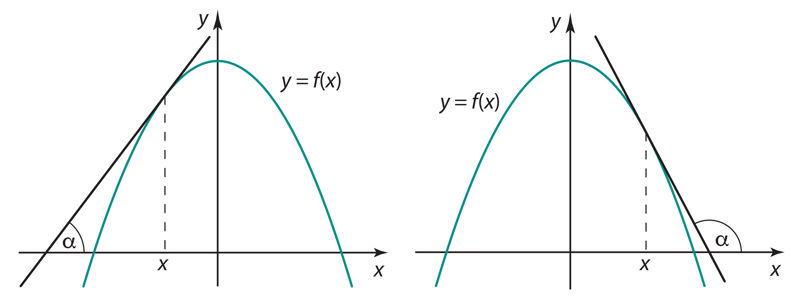
Funktsiooni y = f (x) tuletis on suurus f '(x), millele läheneb funktsiooni muudu ja argumendi muudu jagatis , kui argumendi muut Δx → 0. Funktsiooni tuletis kohal x on võrdne funktsiooni graafikule joonestatud puutuja tõusuga sellel kohal:
Piirväärtuse abil võib funktsiooni tuletist esitada järgmiselt:
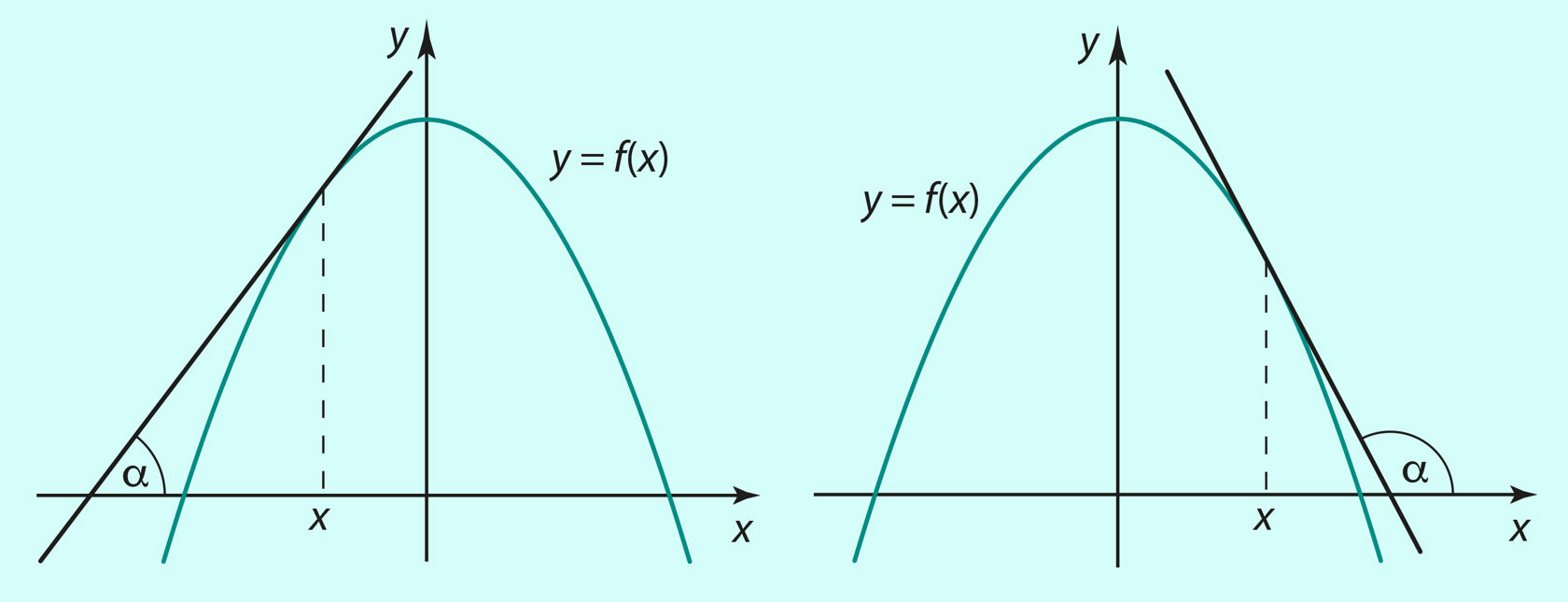 Joon. 1.1 | ||||||