- What do scientists do?
- What is the role of science in the development of society?
- What is technology?
The goal of science is to gain new knowledge
Every day, scientists work to gain new knowledge, make discoveries, and create devices that may benefit people. Our lives have, at least in some areas, become safer and more comfortable: many of us are used to using GPS devices, computers, mobile phones, etcetera. This gives us a way to communicate in a different, new and often easier way with friends anywhere in the world.
Science is both a research process and a body of knowledge that is the result of that research. The goal of scientific research is to get to know the world better, and find answers to the questions of what, why, where, and how things happen. So, science is a way to get to know the world. There are many branches of science that study different fields. For example: linguistics deals with the study and analysis of language, historical science deals with the development of human societies, and educational science deals with education and teaching. These disciplines belong to the science called the humanities.
Biology as a science
Scientific fields that study nature are called natural sciences (e.g. physics, chemistry, biology). Physics studies the most general and fundamental laws in nature, from the cosmic space to the invisible micro-world. Biology is the study of life (bios meaning "life" in Greek). Biology is divided into several branches based on what is being studied.
Think about
- How is biology different from physics?
- Name the sciences that belong under 'natural science'.
- Which field of science do you find most exciting?
- Read about scientific accomplishments from Science Magazine at https://www.science.org/ or from a local science magazine/webpage.
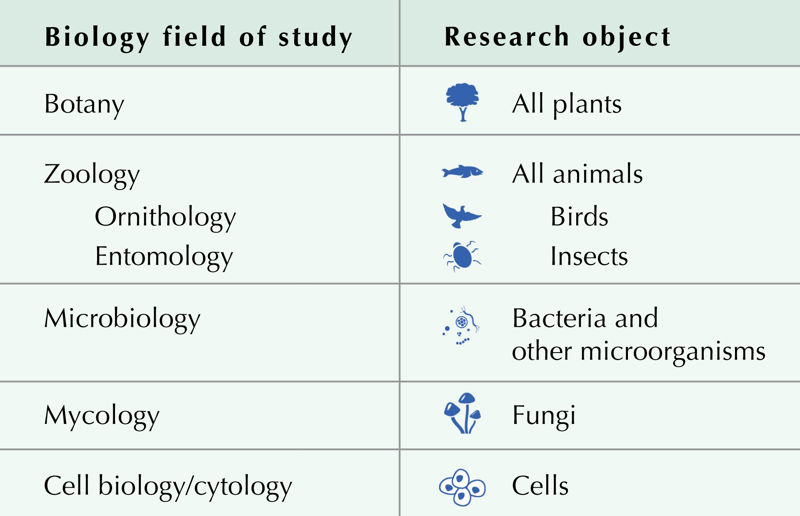
How is science evolving?
Scientific achievements do not come from nowhere, and major discoveries are usually preceded by the long-term work of many scientists. The development of science is based on past achievements. Knowledge that later turns out to be wrong is also needed, because it helps to find the truth. The development of science is a continuous and never-ending process. New knowledge complements existing knowledge, and often corrects it while also providing a better picture of the world.
For example, it was discovered in as early as the 17th century that transferring someone else's blood could save their life. In many cases, however, the transfer failed and the patient died. Further research by scientists provided new information about blood: blood groups were discovered in the early 20th century. New knowledge was also gained about blood clotting and composition. All this made it possible to develop a method that allows blood to be transferred safely.
Better results are often achieved in different fields of science when researchers from several disciplines work together (e.g. physicists, chemists, biologists).
Achievements of science can be used for the benefit of the people
By knowing the laws and natural resources that work in nature, people can build all kinds of equipment and produce helpful results. The desired product can be completed if the necessary tools and skills are available, i.e. the corresponding technology. Technology is a way of producing products. The development of appropriate technology enables the production of complex electronic devices and other machinery. To make yogurt from milk, salt from seawater, starch from potatoes, or popcorn from corn, the right technology must also be used. The depletion of oil reserves has forced people to develop new technologies for the production of automotive fuel, such as from rapeseed or corn.
Scientists investigate their research field's topics to gain new knowledge about them. However, sometimes technology uses the achievements of science to solve practical problems too, such as the development of products or services that humans need.


Technology depends on scientific progress, and the development of technology, in turn, contributes to the development of science. For example, scientific advances in physics enabled engineers to invent an electron microscope that magnifies hundreds of times more than a conventional light microscope. By using an electron microscope, scientists have made new discoveries, for example in the field of construction and/or structure of cell parts.
Although technology aims to improve human life, some advances in technology have had detrimental effects. For example, the widely used insecticide called DDT proved to be a dangerous poison that caused disease in humans and animals, and is therefore banned in many countries.
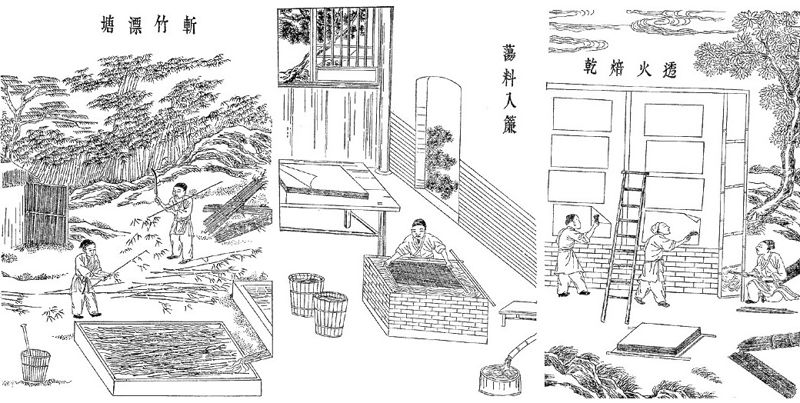
Bonus: The first paper-making technology
The paper-making technology originated in ancient China, and is over 2,000 years old. Initially, hemp fibres, bamboo, bark, cotton rags, etc., were used as raw materials. This material was allowed to soak and decompose, then it was crushed until a semi-liquid fibrous mass was obtained. The paper sheets were pressed from the mass and then dried. The writing paper was treated with glue before drying. It was not until the middle of the 19th century that wood was used as a raw material. The resulting paper was cheaper but of poorer quality.

Think about
- How are science and technology related?
Not everything that looks like science is science
Sometimes more weight is given to the claims that present themselves as scientific, although those claims may not be true. Presenting unverified data as scientific facts can cause a lot of damage. For example, unscientific dietary recommendations or treatments can be dangerous to people's health.
Pseudoscience is reminiscent of science, but is based on assumptions and facts that have not been verified. Scientists arrive to scientifically proven facts by using a scientific method, and most importantly, repeating tests several times. The credibility of a scientific fact increases when other researchers reach the same conclusion. Pseudosciences are often based on select individual cases. A lack of knowledge and the will to think independently can be related to how much a person believes in pseudoscience. There is still much undiscovered knowledge in the world, but a distinction must be made between scientifically proven legitimacy, and scientifically unproven assumptions and beliefs.

Think about
- What makes pseudoscience different from science?
Why do we need knowledge of biology?
Biologists work not only as scientists, but also in many other fields: nature and environmental protection, education, fishing, hunting, and more. In addition to biologists, medical professionals and many other professionals also need biological knowledge.
Microbiologists work, for example, in food laboratories, where they work together with chemists to analyse food samples to see if they are suitable for consuming. It is important that only high-quality food reaches people– food that does not contain disease-causing microorganisms, and is not contaminated with toxic substances such as insecticides. In the food industry, they assess the safety of food, but they also monitor the microbial production of various products: yogurt, pickles, etc. Microbiologists also participate in environmental research– they perform analyses of drinking and pool water, sewage sludge, soil, etc.
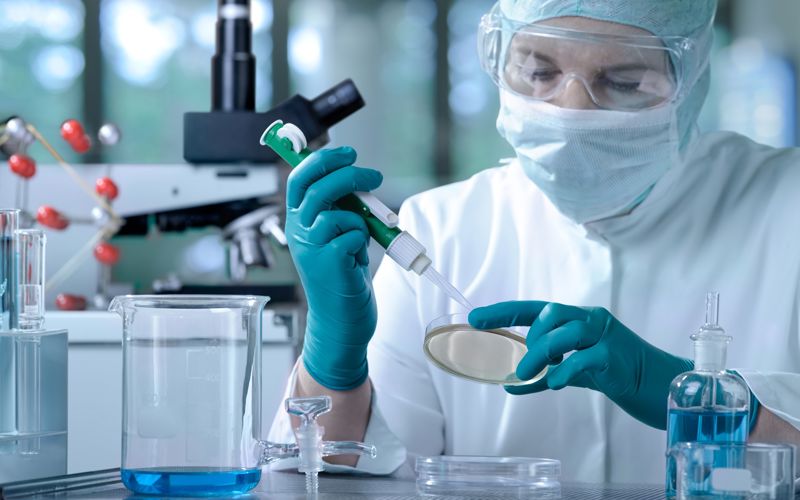

Biomedicine is a discipline that combines biology and medicine. In order to better understand and influence what is happening in humans, cutting-edge science is able to study the human body at the molecular level. For example, some European researchers are working with other researchers to develop a vaccine against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that would presumably protect people from this pathogen. HIV causes a serious illness, AIDS, which makes a person susceptible to other infectious diseases and cancer.
Fish farmers need to have a thorough knowledge of fish biology in order to create suitable conditions for fish farming, and to prevent diseases that endanger them. Fish are mostly farmed for human consumption, but also to strengthen or restore wild populations. Many fish farms in Europe, and all over the world, raise fish juveniles from salmon and sea trout eggs. At the appropriate age, they are released into local rivers in order to increase fish stocks there. Before being released, juveniles are tagged so that scientists know how many of them survive, where they migrate, how they grow, and how many are caught.

Nature conservation workers take care of the conservation of endangered animal species and communities. Thorough knowledge of zoology and botany help them decide how to protect animal and plant species wisely. For example, they gather information on rare eagle species and provide guidance on how to improve and increase the numbers of these birds. Nature conservation helps to preserve the diversity of life.
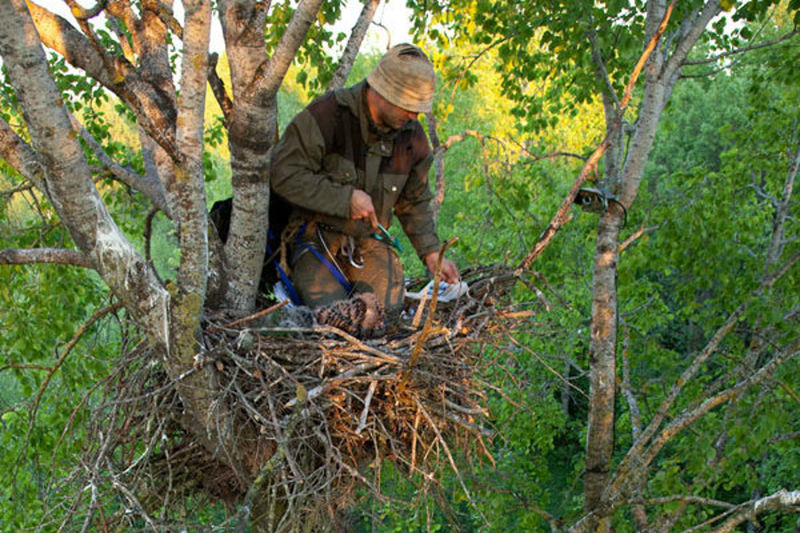

People involved in forestry need knowledge of both biology and forestry. They must be familiar with the forest biota, the characteristics of this ecosystem, the technology of primary wood processing, and also with the legislation that regard forestry. They grow and maintain forests where they get the wood they need. Intelligent management ensures that forests are preserved and that timber production is sustainable.

Marine biologists study marine life, and monitor the state of the water. They assess the size of fish stocks, and make recommendations for fishing planning. Together with other professionals, they assess the potential impacts of the construction of offshore wind farms, pipelines, and cables on the marine environment. Knowledge of the state of marine life for the guidance of human activities is important for the conservation of species.

Plant breeders create new plant varieties that give good yields, are disease-resistant, and/or have good taste. For example, new varieties of potatoes, cereals, and vegetables are bred at many European plant breeding institutes. Scientists from several countries often work together to breed one variety. For example, in more northern latitudes, new wheat varieties have been developed, which are suitable for cultivation even in a cooler climate. These varieties can also be used for producing good bread flour.

Think about
- With which type(s) of natural scientist does a marine biologist need to work with to study the state of the Atlantic Ocean or the Mediterranean Sea? (You can also pick a more local example of a sea or another big water body instead.)
Research
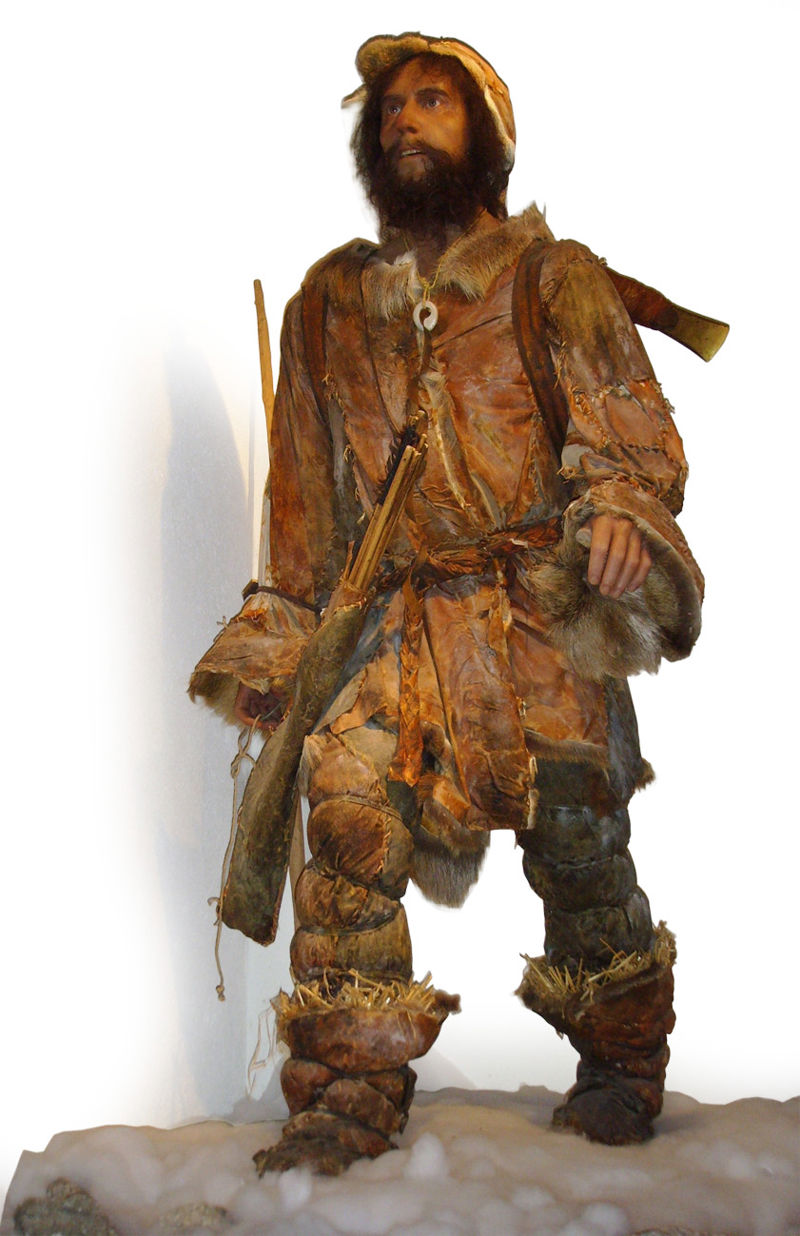
''Ice man'' Ötzi
In 1991, hikers found a human body in a glacier melting in the Alps, which turned out to be over 5,000 years old. This corpse of a man from the Stone Age was relatively well preserved in the ice and turned into a mummy. It is currently in a special museum in Bolzano, Italy. The discovery became a real sensation in the world of science. 147 researchers from 11 countries began to study it using state-of-the-art methods. Medical scientists, botanists, mycologists, geneticists, archaeologists, and many others were interested in the man himself, his physique, injuries, stomach contents, signs of illness, as well as clothing, food, weapons, and other equipment he had with him. For example, there were pieces of birch polypore/bracket thrown or fallen on a fur strip of the ''ice man''. Because birch polypore contains bactericidal substances and have healing properties, microbiologists have speculated that it was a prehistoric "travel pharmacy." The man also had a stone dagger with him, and animal tendons were used to secure its handle, which was made of ash tree wood.
You can read more about the ''ice man'' Ötzi from the following book: Konrad Spindler, The Man in the Ice.

Questions and tasks
- Discuss with the class about what biological knowledge students your age may have had 100 years ago. Compared to the knowledge you have, what might they have known more about, and what subjects or topics might they have known less about?
- What technological achievements have you used today? Give examples.
- What knowledge of biology does a dental technician need in order to make dentures?
- Describe a situation to the class, or your partner, where you or a member of your family needed biological knowledge.
- What knowledge of biology does a person growing houseplants or raising pets need?
- Explain why a prediction based on the lines on your hand cannot be considered scientific.
Important terms
- science– activities aimed at getting to know the world; it is both a research process and a body of knowledge that is generated as a result of that research
- natural sciences– sciences that research and deal with nature
- biology– science that deals with wildlife research
- technology– the way products are made
