The natural environment consists of biotic and abiotic factors. Abiotic factors are topography, hydrology, and atmosphere; biotic factors are flora, fauna, and humans. The development of life on Earth takes place through nature and human activities. In the past, nature determined the story of humans and society, but now humans influence the environment and change life on Earth, often faster than nature itself can.
What does a geographer do?
Geography is the study of Earth. The word "geography" comes from Greek and means 'a description of the earth'.
In the old days, geographers only described the earth and its different regions. Although the Age of Discovery is long gone, knowledge of geography will continue to be necessary. Geographers look at the environment and get to know it. They are interested in natural and human phenomena, the globe's regional differences, and what causes them. Landscapes and human societies are studied, people are interviewed, and the data collected is analysed.

The main interest of geography is the whole globe: continents, countries, counties, cities, municipalities, and even smaller areas. Research results are often presented on maps, one of the geographers' most critical tools. In the past, geographers mainly studied where a region in the world is, its nature, and its people.

Today, however, geographers are also interested in why one region differs from another, how nature and society are interconnected, and what causes changes in different areas' natural and human activities. Geography also aims to draw people's attention to environmental problems, and alleviate the damage that has already occurred.
Physical geography describes and explains the nature of biotic and abiotic factors, the processes and phenomena occurring in nature, and the interactions between natural phenomena. Physical geographers study mountains, rivers, topography, vegetation, and climate.
Human geography studies people and the specifics of human activities in different regions. It addresses, for example, population, economic and cultural issues, and also explores cities and rural areas.
How do geographers collect data?
Geographers collect data using increasingly modern technology. For example, sensitive and sophisticated measuring instruments measure biotic and abiotic factors and record changes in land, water, and air.
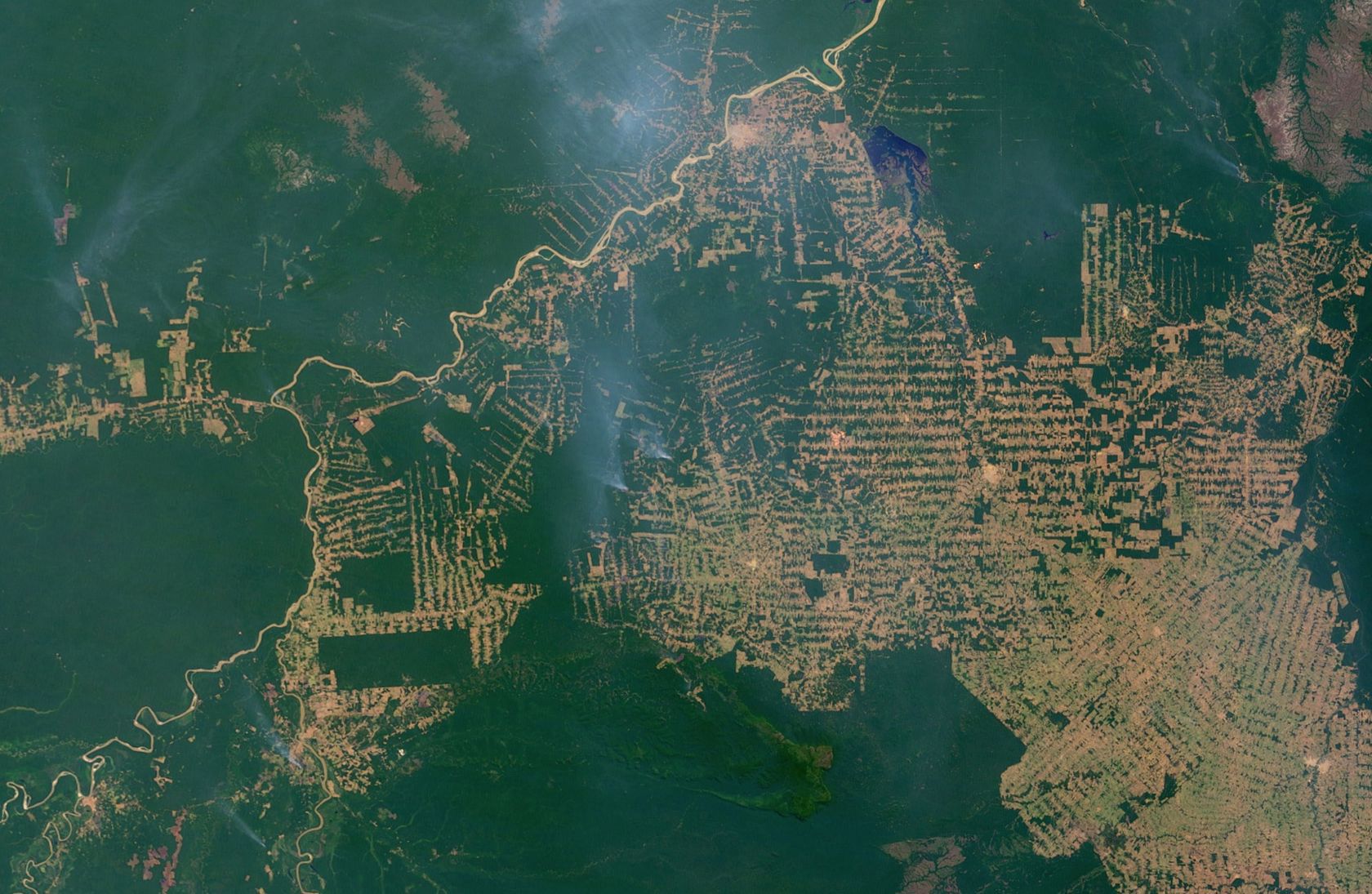
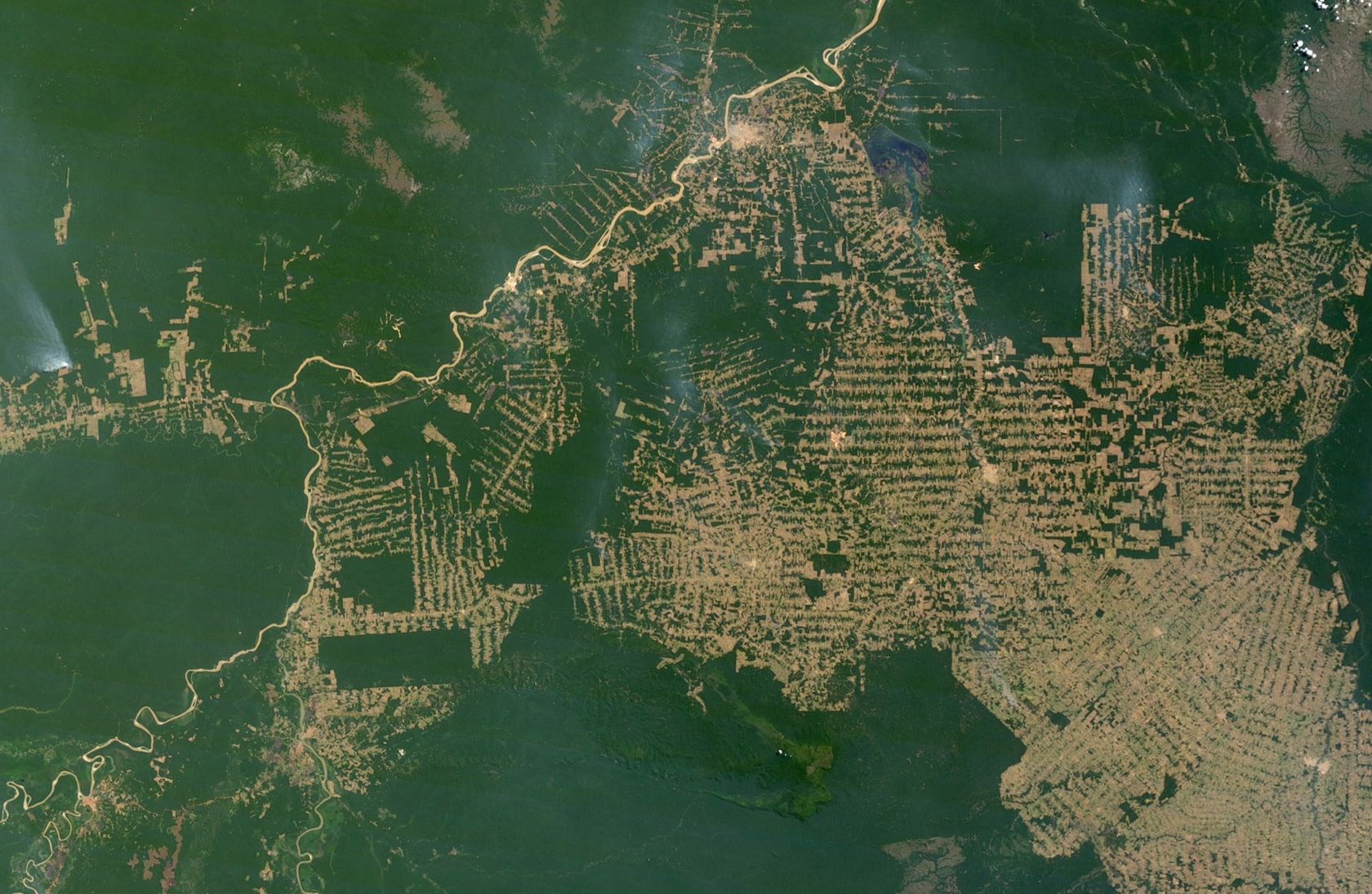
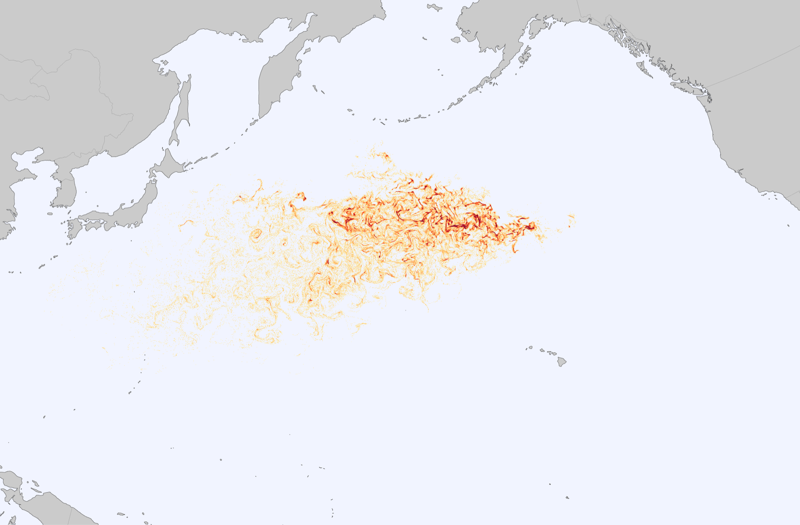
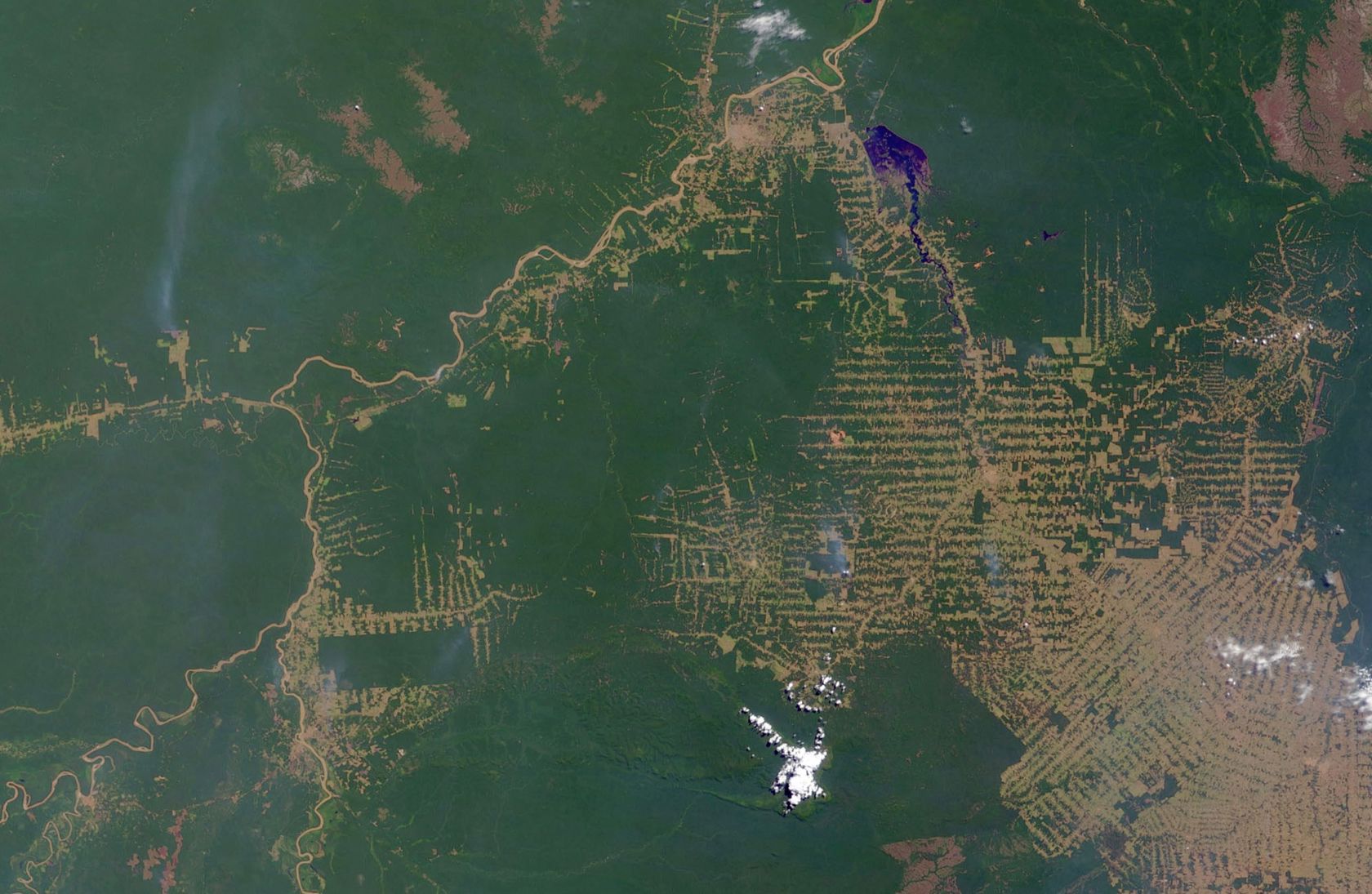
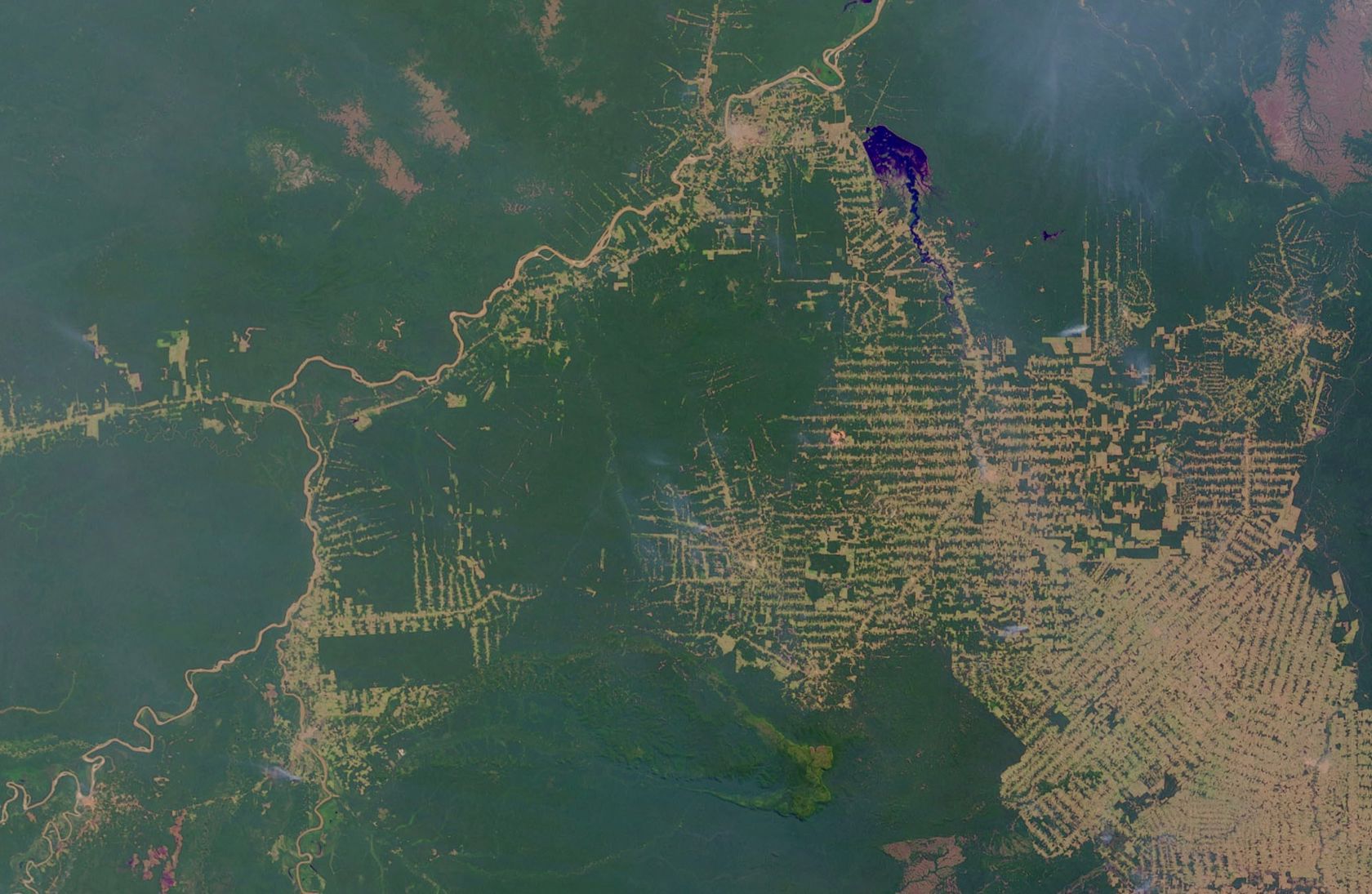
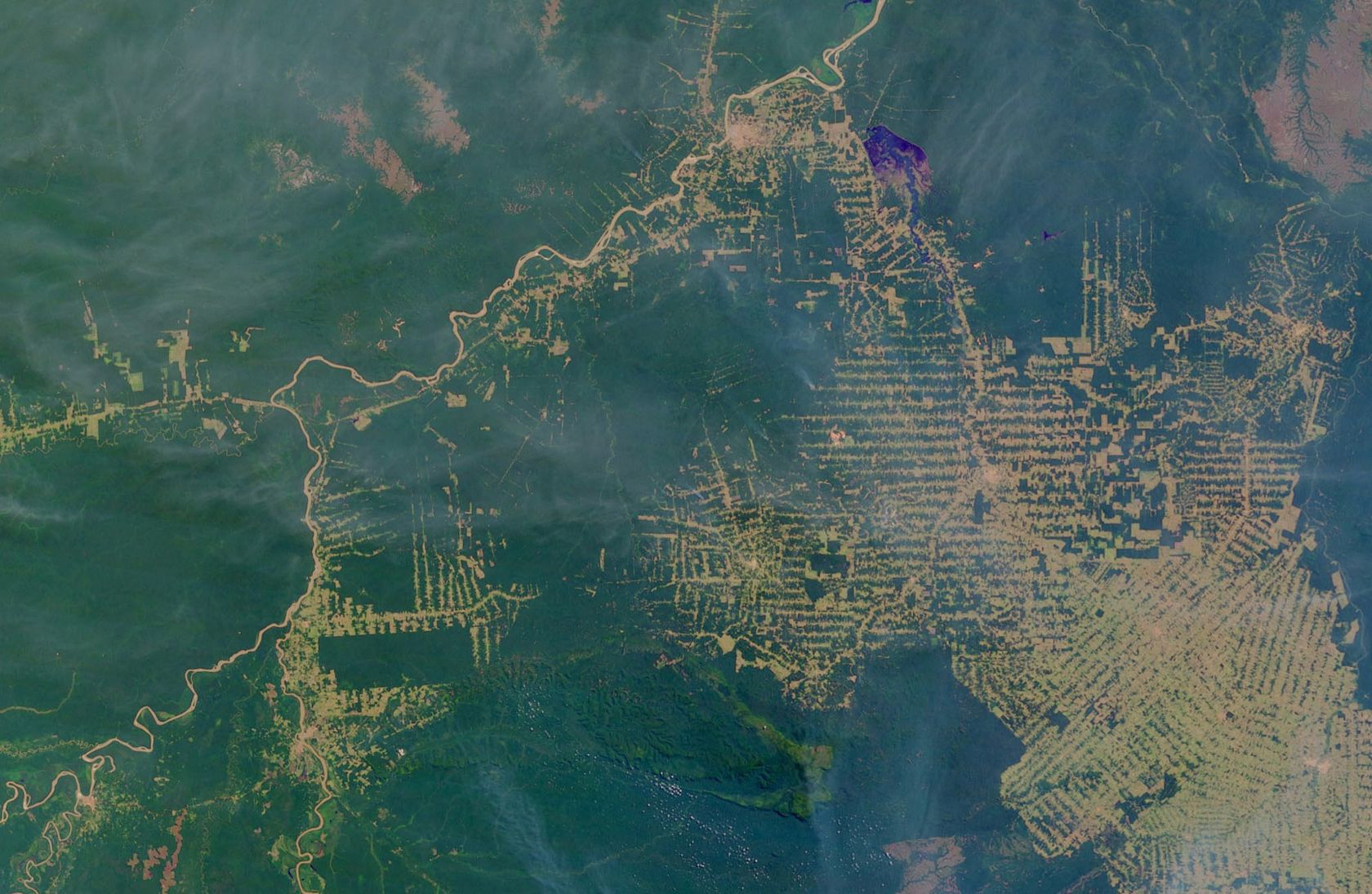
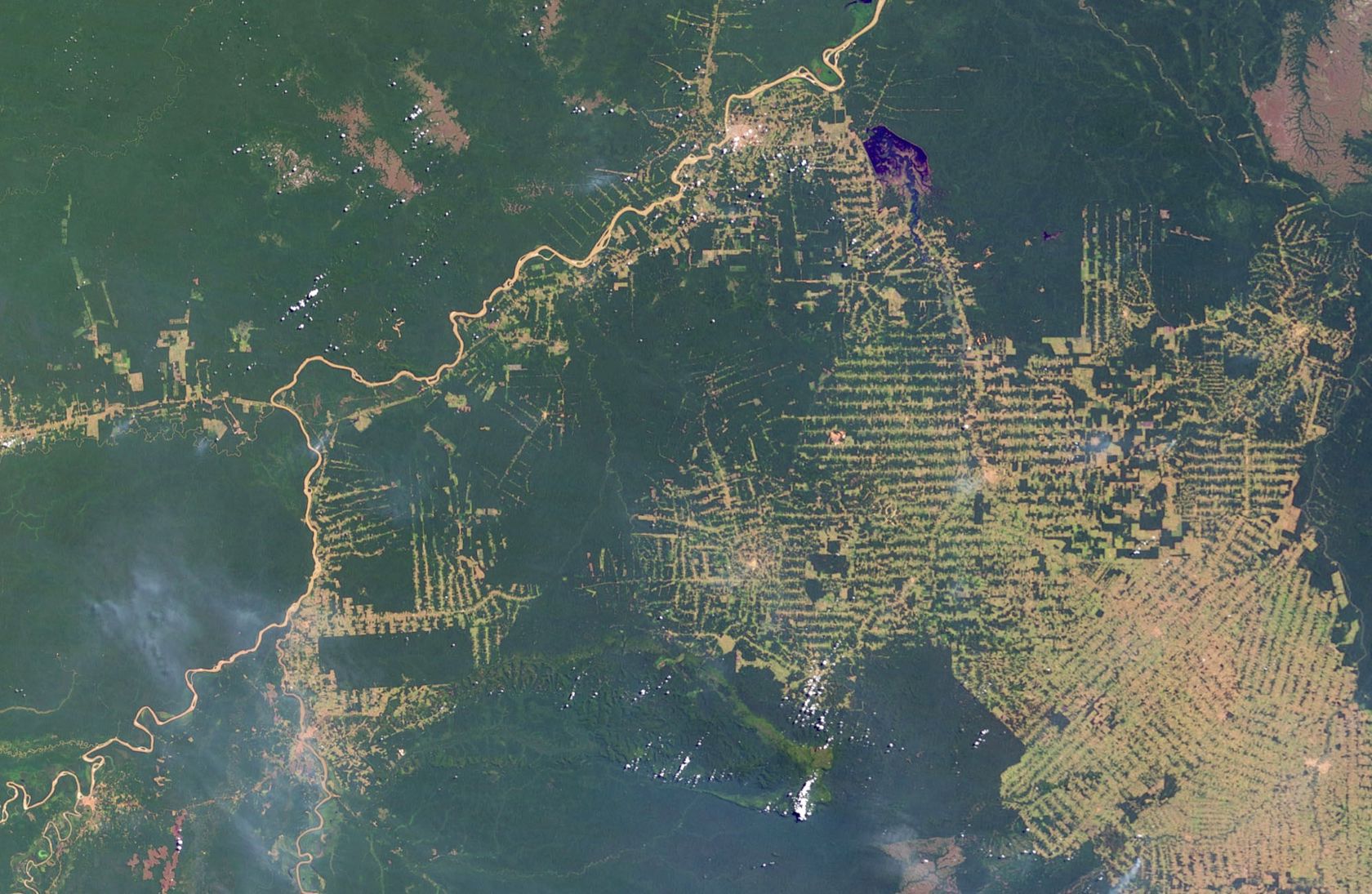
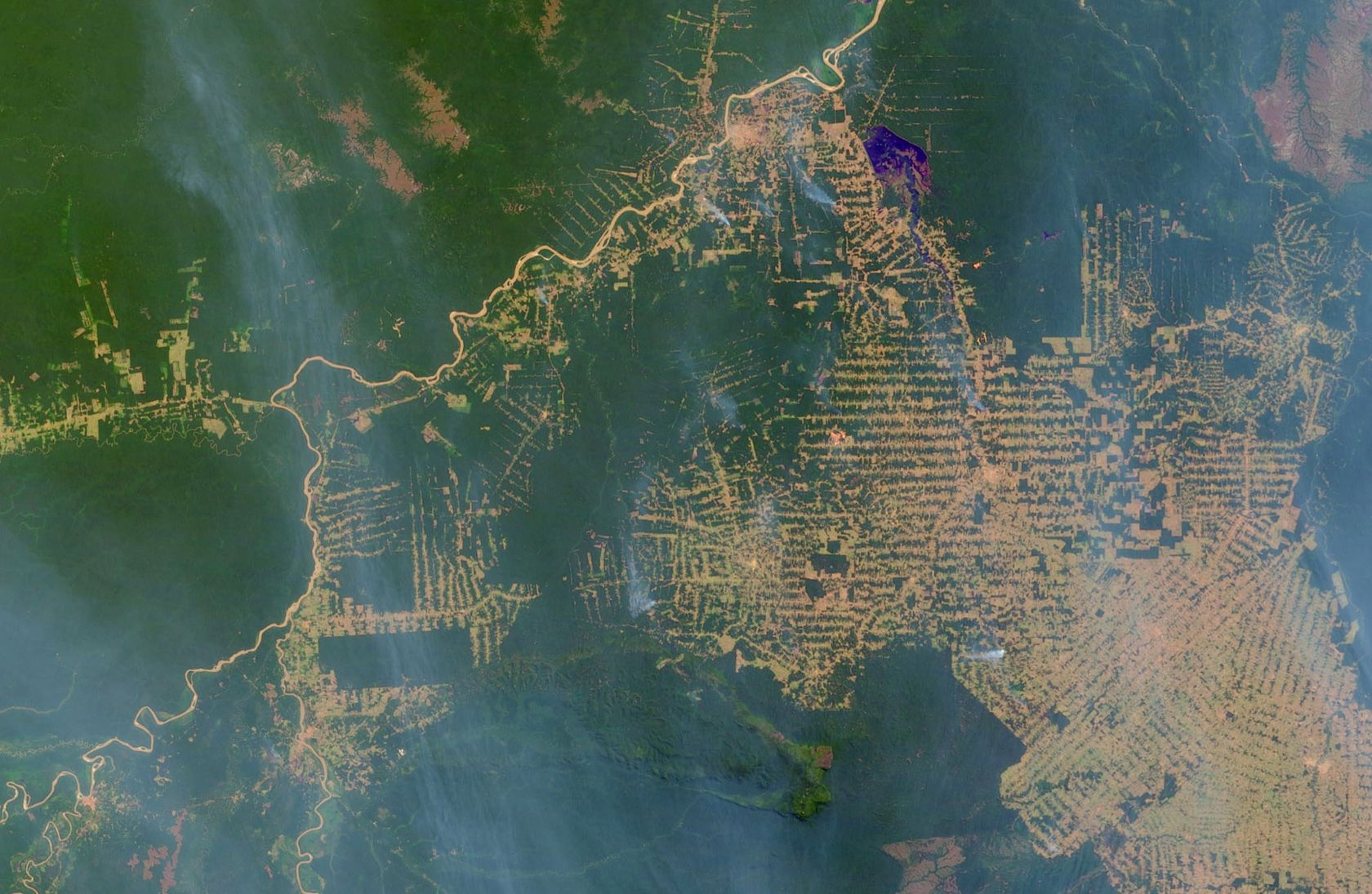
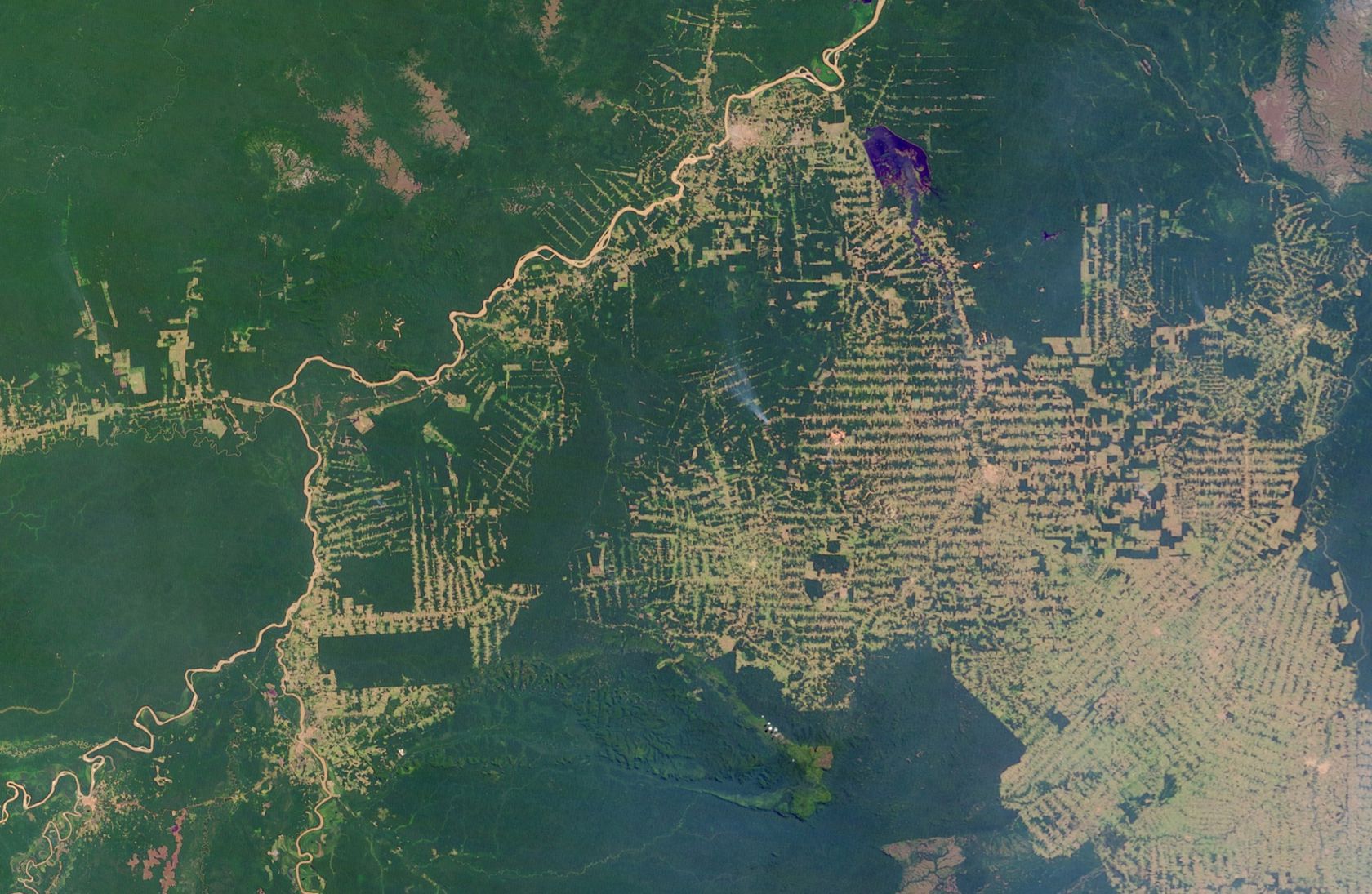
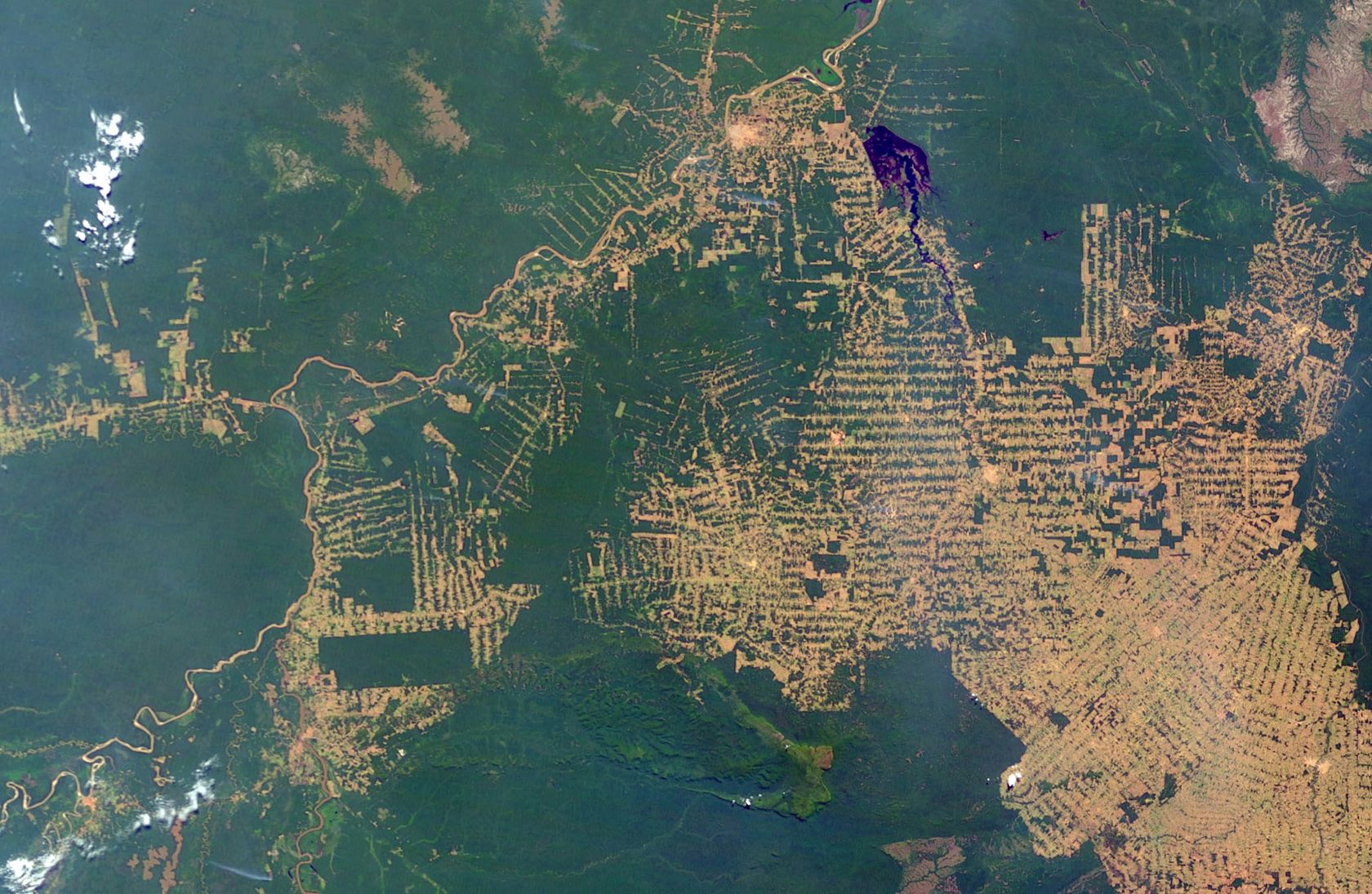
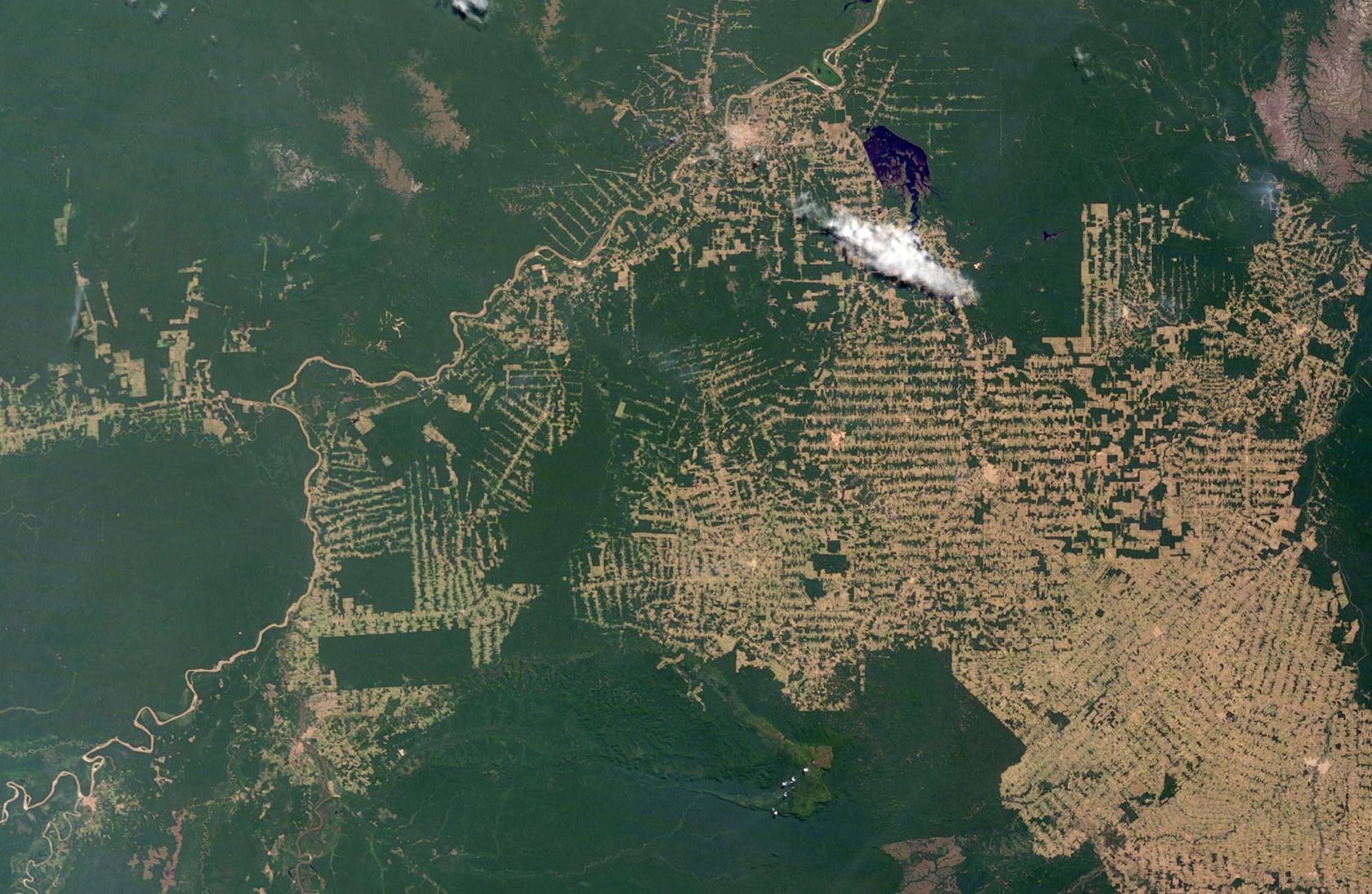
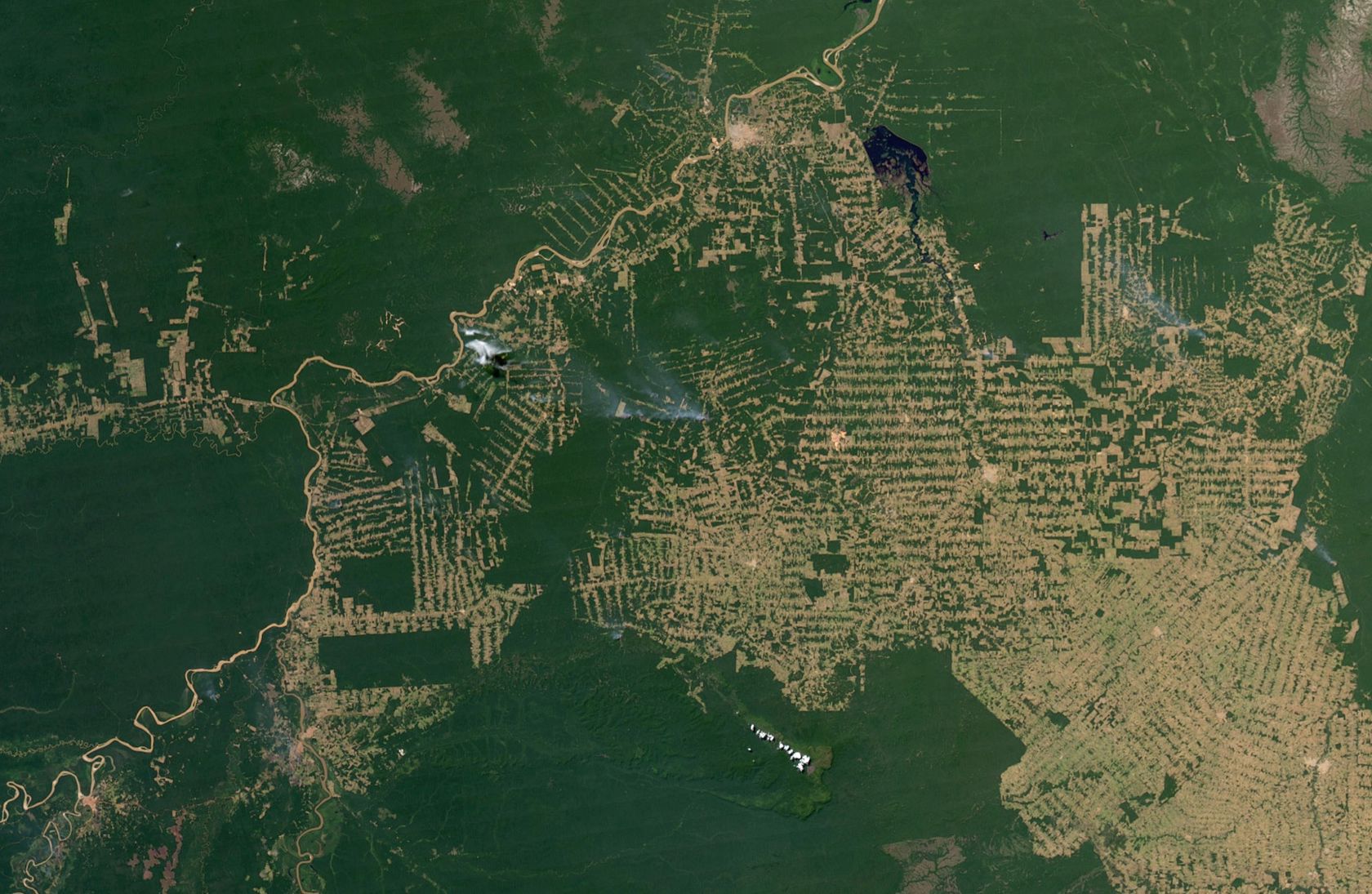
The satellites orbiting the earth capture the earth's surface with great precision. Satellite imagery examines environmental change in large areas, such as deforestation in South America, desertification in Africa, or the world's urbanisation. Powerful computers quickly transmit research results wherever there is an Internet connection.
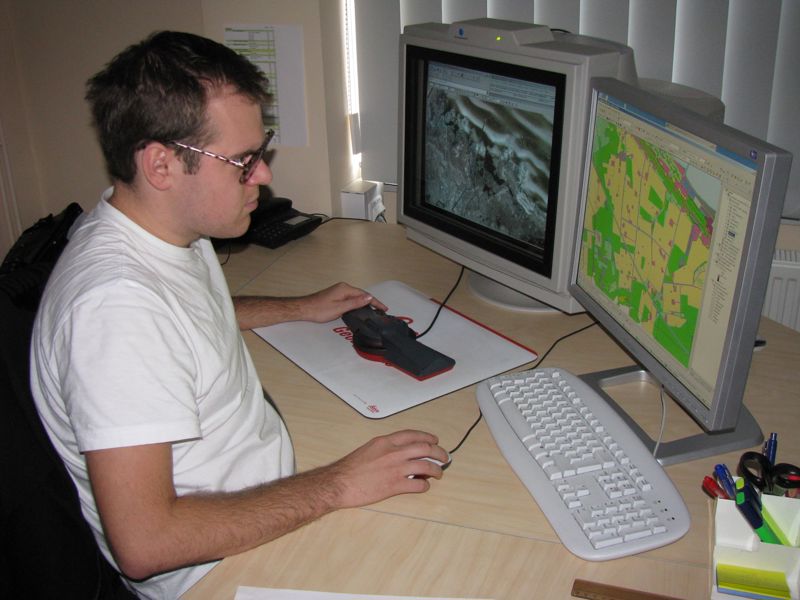
The technology allows you to make maps from any region of the world. Computer cards that can be viewed online are used in addition to paper maps.
However, traditional research methods have not lost their importance. For example, geographers still make weather observations and natural measurements, map the landscape, and conduct surveys.
Think
- How does the increasing use of computers affect geographical research? Why?
Think
- What could be the causes of deforestation?
- What could be the consequences of deforestation?
- to study processes in the air
- to study processes and changes on the ground
- to determine animal species
- to explore other planets
How are continents and oceans distributed on Earth?
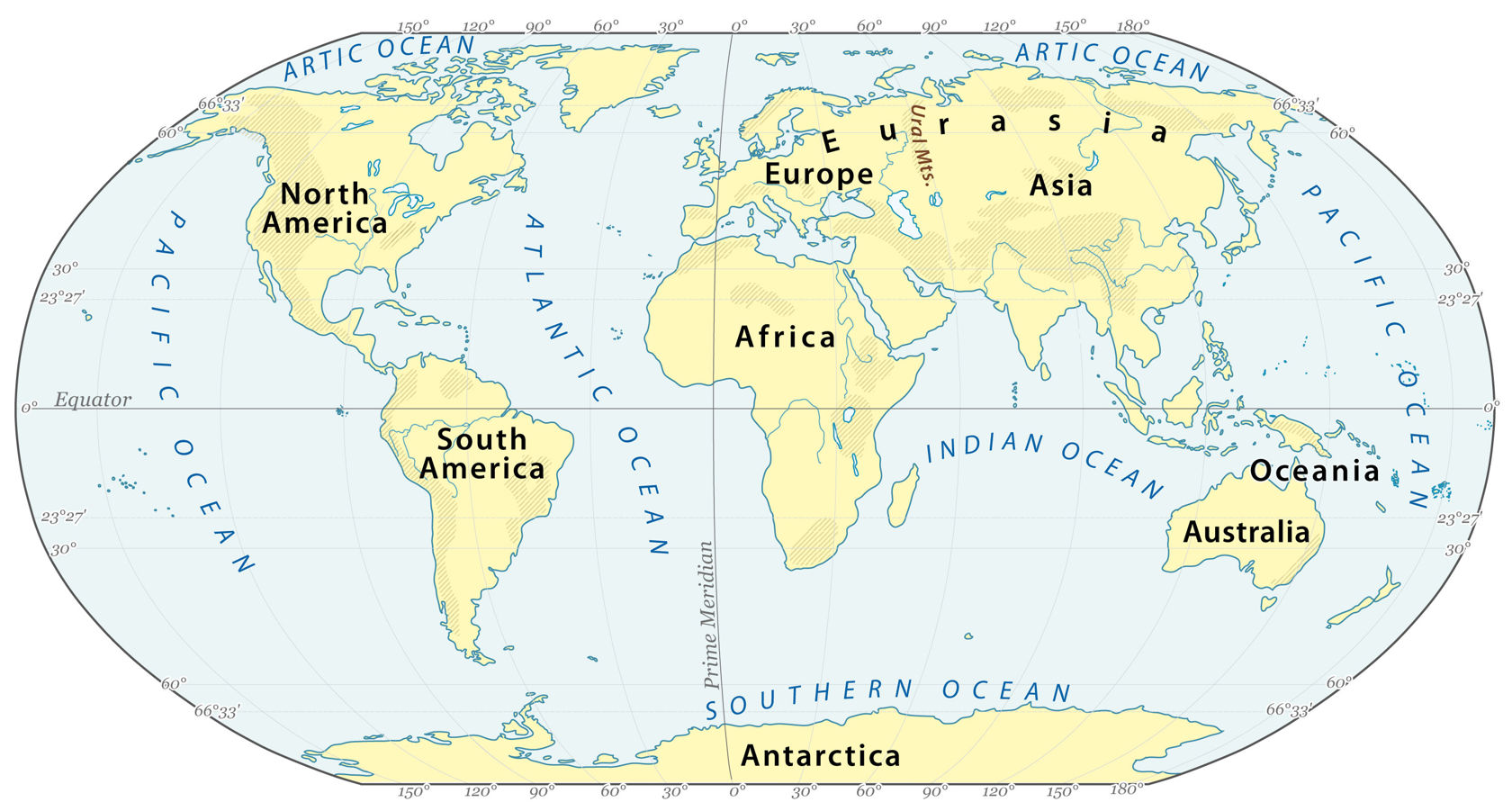
Millions of years of natural processes formed oceanic trenches and the largest continents of the earth. Ordered from largest in the area to smallest, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these. For example, some systems include Eurasia or America as single continents.
The continents vary greatly in size: the largest continent, Eurasia, is about seven times larger than the smallest, Australia. On the other hand, Australia is more than three times the size of Greenland, the world's largest island.
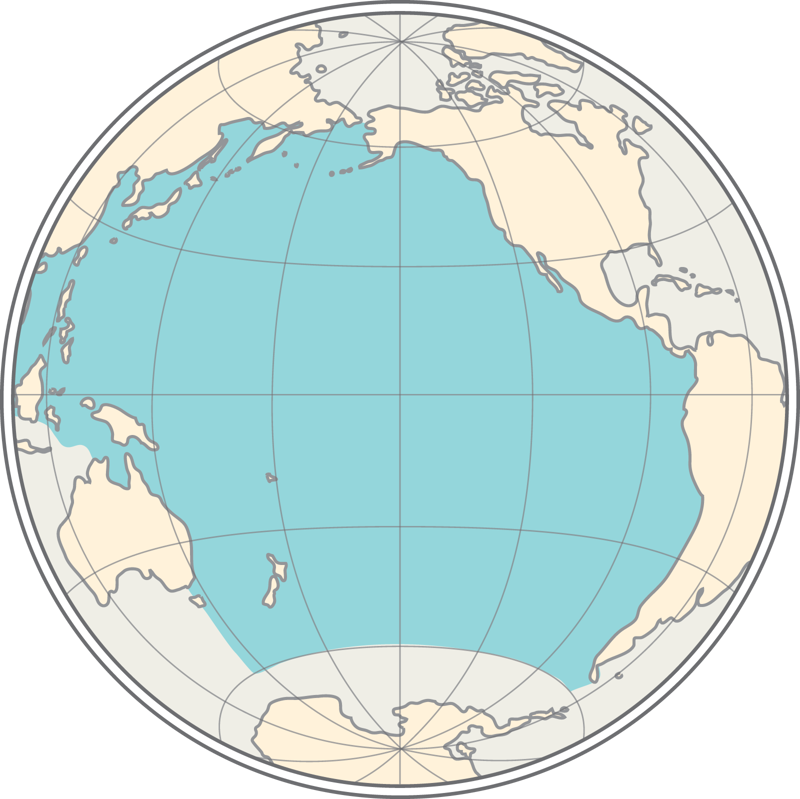
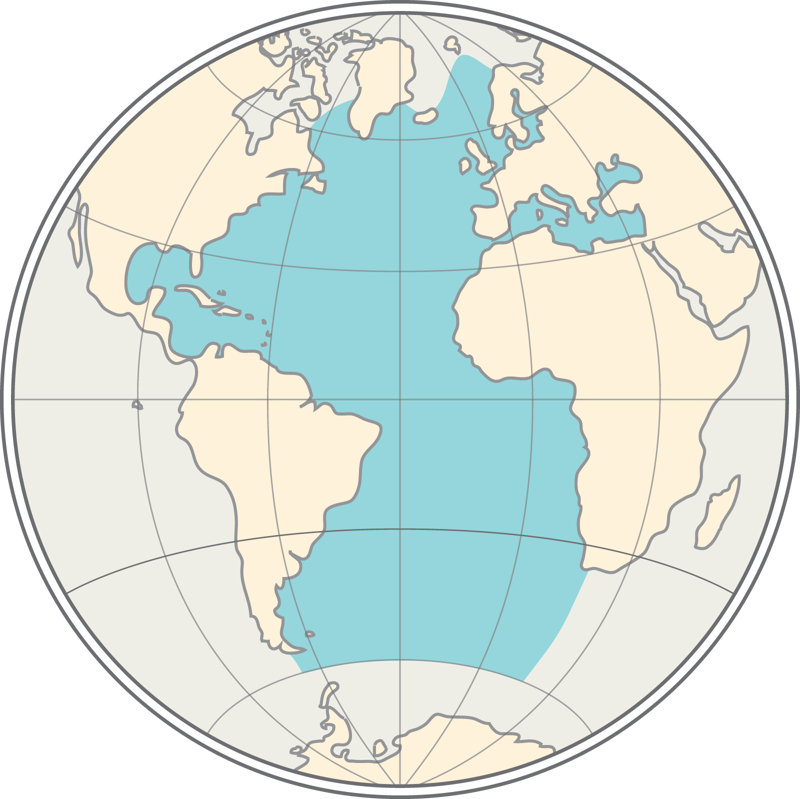
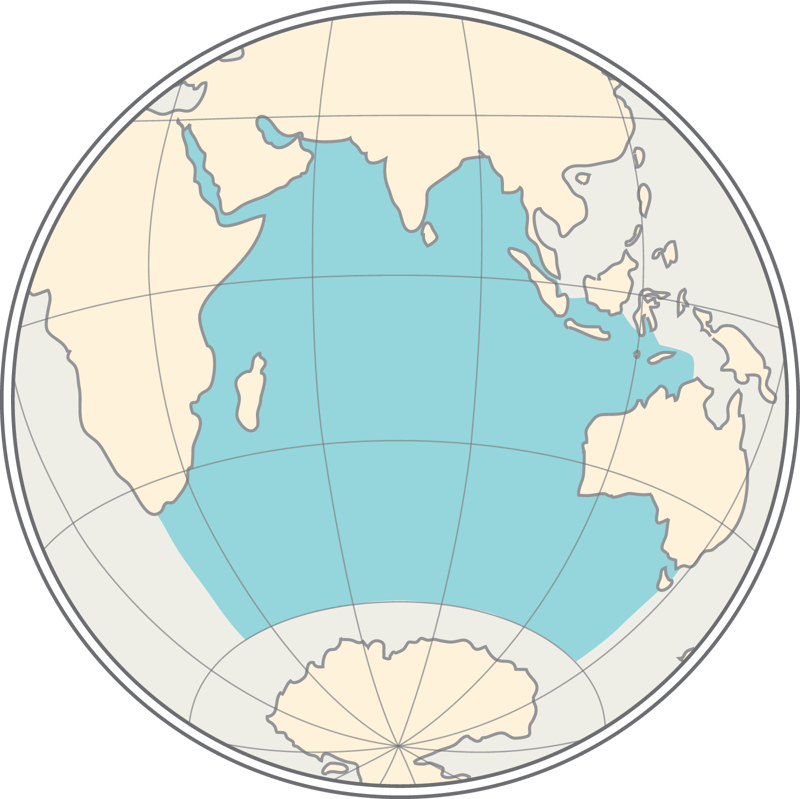
The continents are separated mainly by oceans, seas, and straits, forming the world ocean.
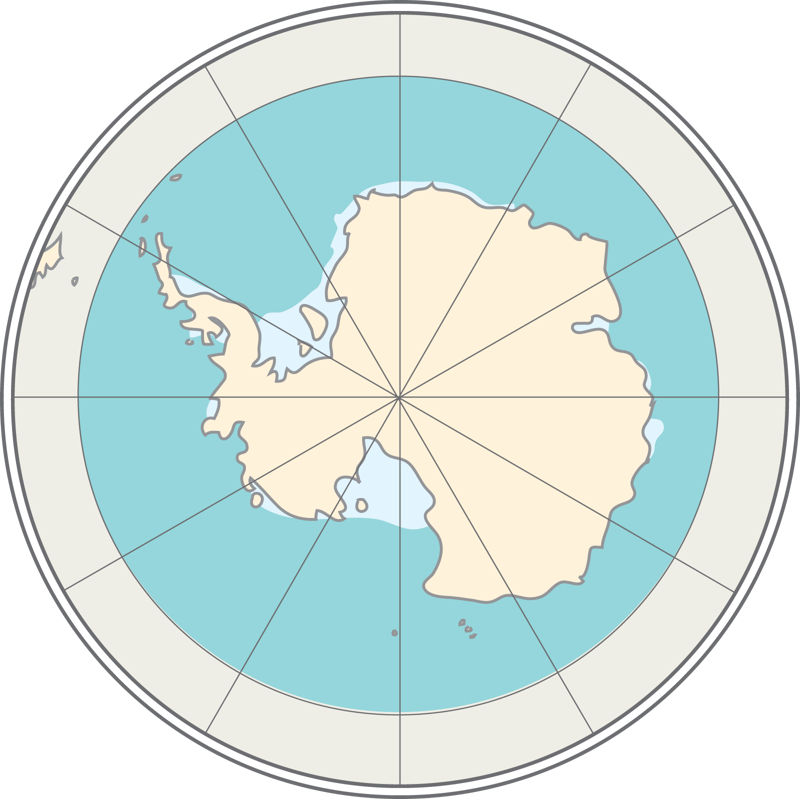
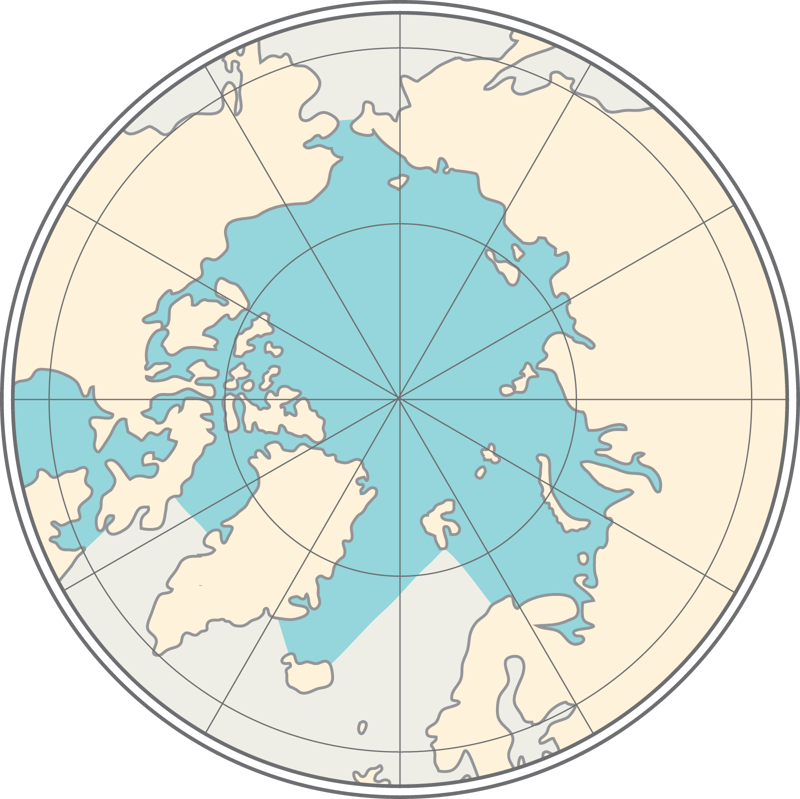
The world ocean is divided into five oceans: the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Arctic Ocean, and the Southern Ocean.
- Africa
- Eurasia
- Australia
- Antarctica
Continents are generally considered to be large that are surrounded by. The largest continent is and the smallest continent is. Sometimes and Asia are considered as a single continent called.